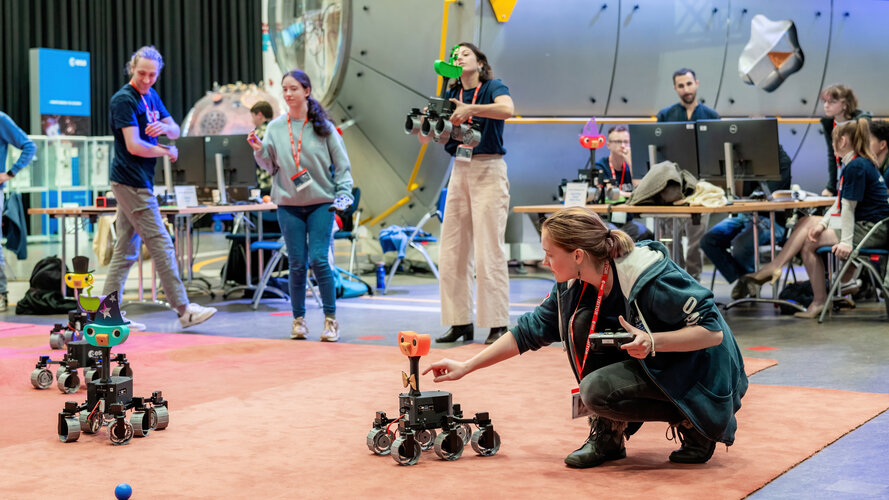Automation and Robotics Laboratories
ESA's Automation and Robotics group is responsible for the creation and maintenance of an industrial technology base for the automation and remote control of space based operations. As such, the domain of competence of the group includes the specification and control of space robotics systems (from manipulators to autonomous vehicles) and laboratory supporting automation and robotics in manned and unmanned missions. ESA’s Automation and Robotics Laboratories (ARL) are:
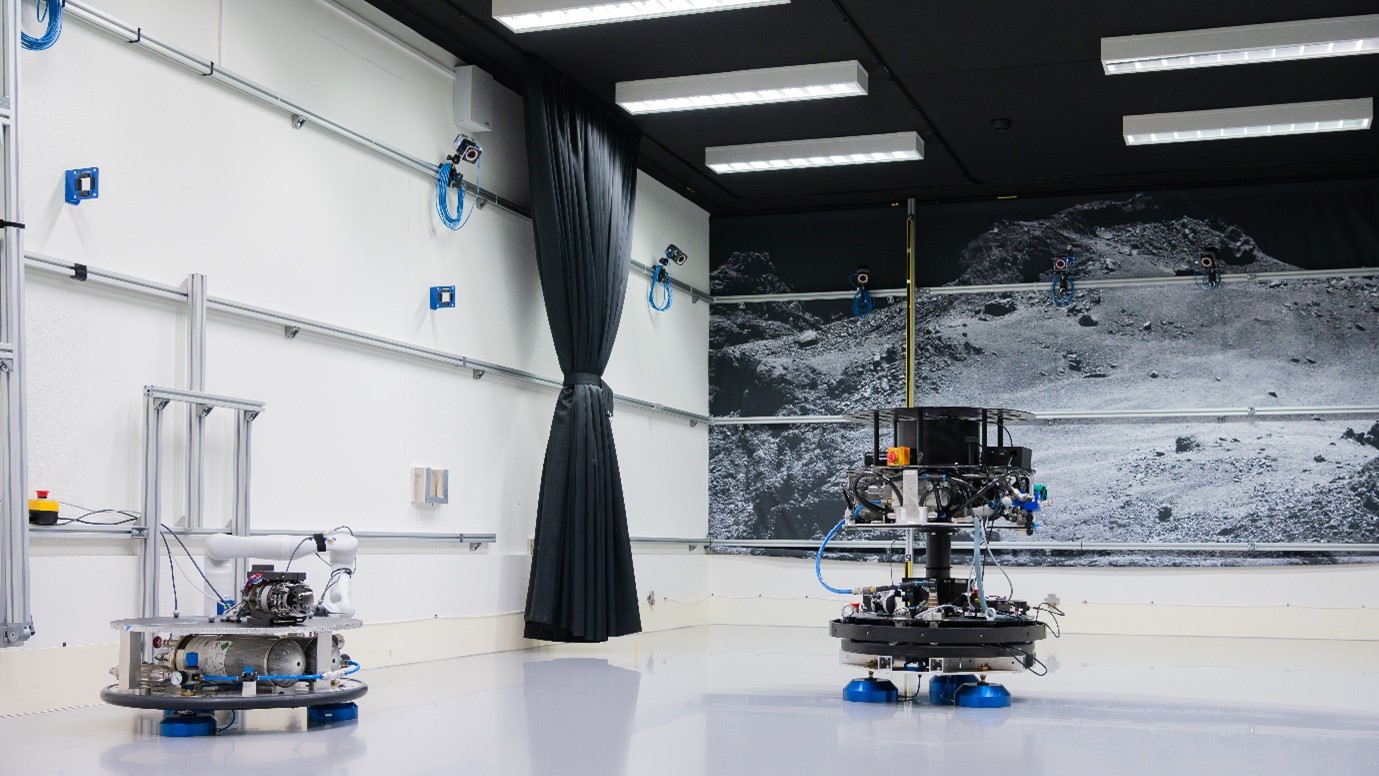
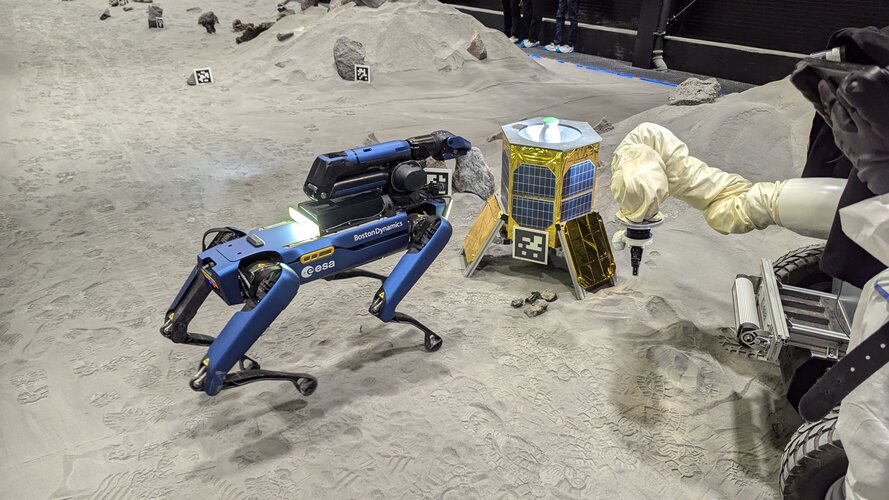
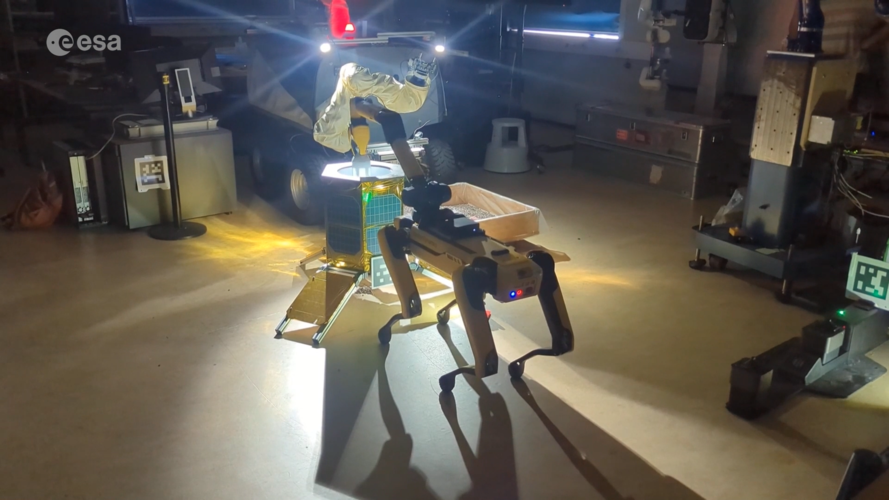
- The Orbital Robotics Lab (ORL) addressing the use of robots in free space where interaction with man-made (spacecraft) or natural (asteroid) objects is complicated by little or null gravity.
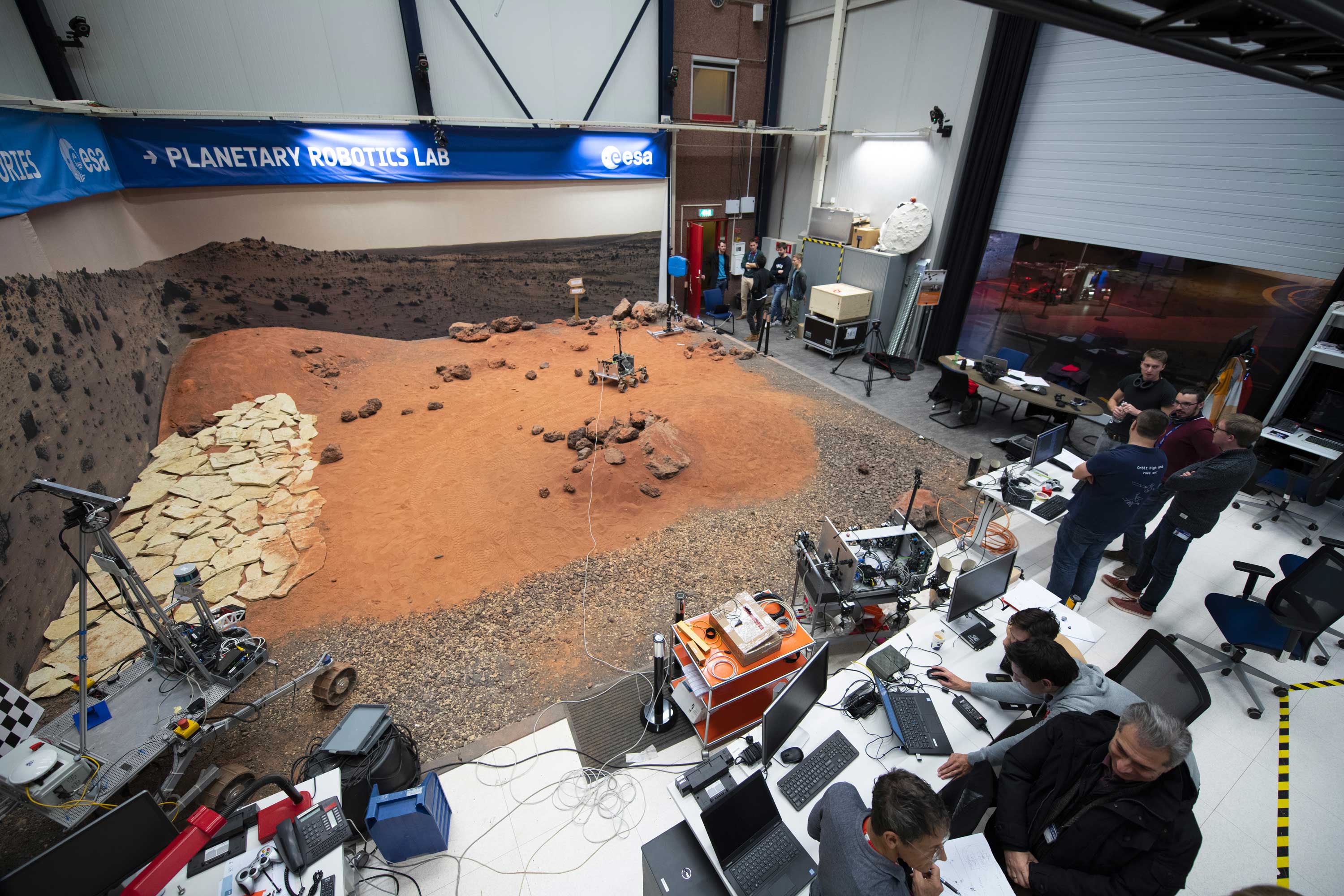
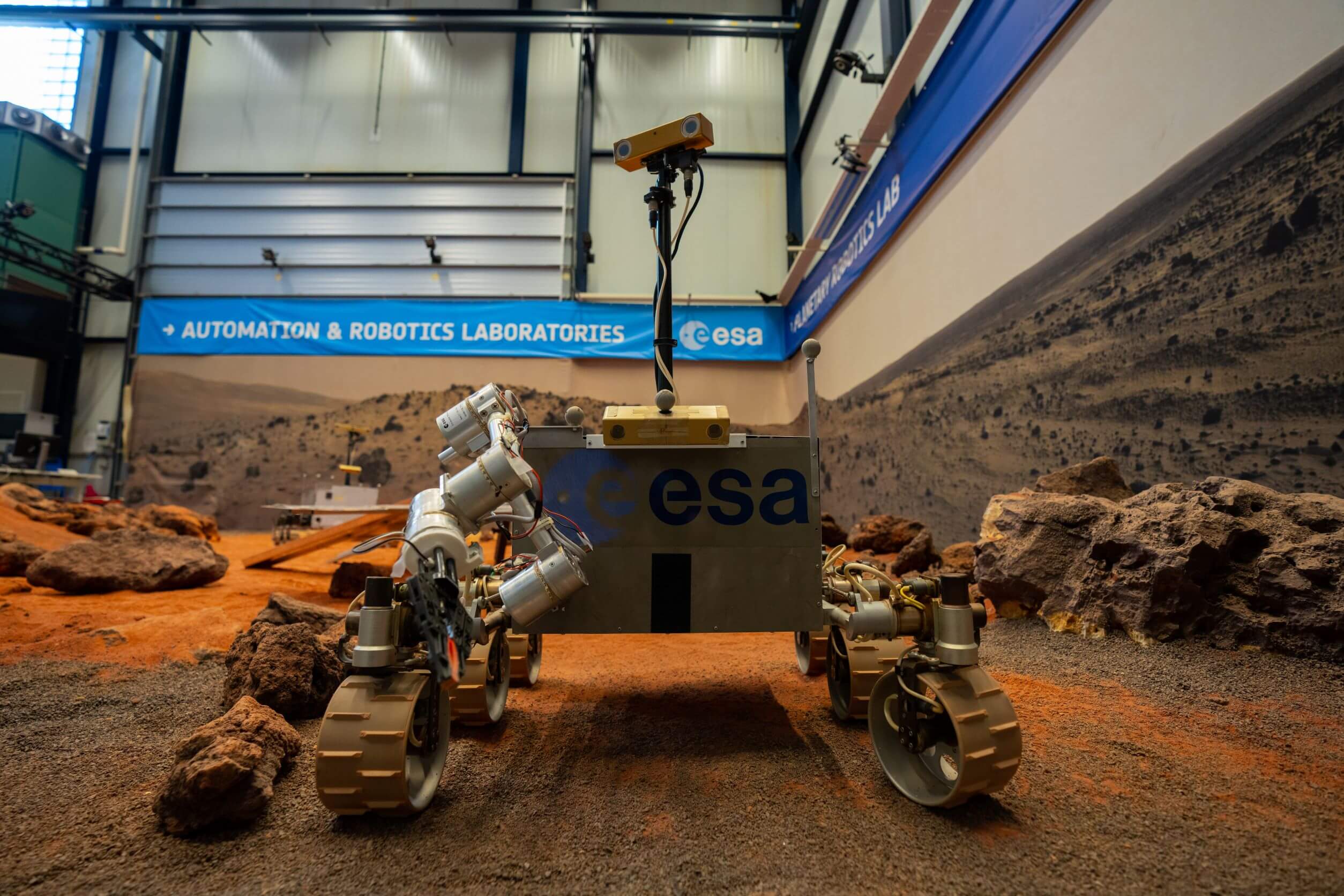
- The Planetary Robotics Lab (PRL) focuses on robot roaming on the surface of Moon and Mars, where interaction with the surface, regolith, rocks or boulders requires specific locomotion and navigation approaches.
- The Human Robotics Interaction Lab (HRI) (formerly known as Telerobotics and Haptics Lab) is addressing the means of interaction between humans and remote or co-located robots with a special focus on real-time teleoperation.
The ARL is covered by the overall ISO9001:2008 certification.
For testing requests, access to lab facilities, training and consultancy services, please refer to:

Orbital Robotics Lab
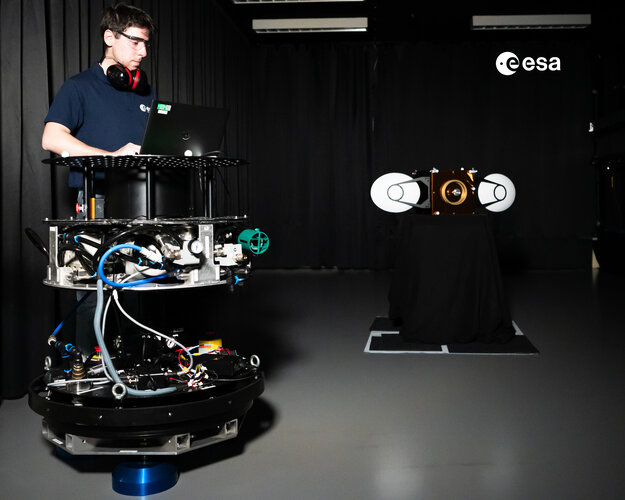
The Laboratory specialises in the problems and related solutions, stemming from the use of robots in orbit (e.g. satellite/station servicing, debris removal) or in sampling in very low gravity environments (e.g. Phobos/meteroid/comet sampling).
The lab provides tools to research, develop and validate the means to cope with proximity manoeuvring, free-space trajectory planning, navigation and localisation, free-floating contact dynamics, and low-gravity sampling. As the problems of contact dynamics and motion in free space are also faced by astronauts in orbits, the ORL can also help in the training of crew by providing a physical simulation environment.
The lab is jointly funded and operated with the GNC test facilities in order to increase synergies between the topics in GNC and robotics.
All laboratory facilities can be remotely operated through the laboratory’s local network with great attention placed on data synchronisation and repeatability to assure top quality test results.
Three floating systems are available:
- REACSA/ACROBAT has an adjustable weight between 150-250 kg and allows payloads up to 100 kg. Features add-on air thrusters and reaction wheel for simulating a spacecraft’s AOCS
- MANTIS weights 35 kg and allows payloads up to 100 kg
- ROOTLESS2 is for the smallest payloads, decoupling the inertia of the system from the floating platform
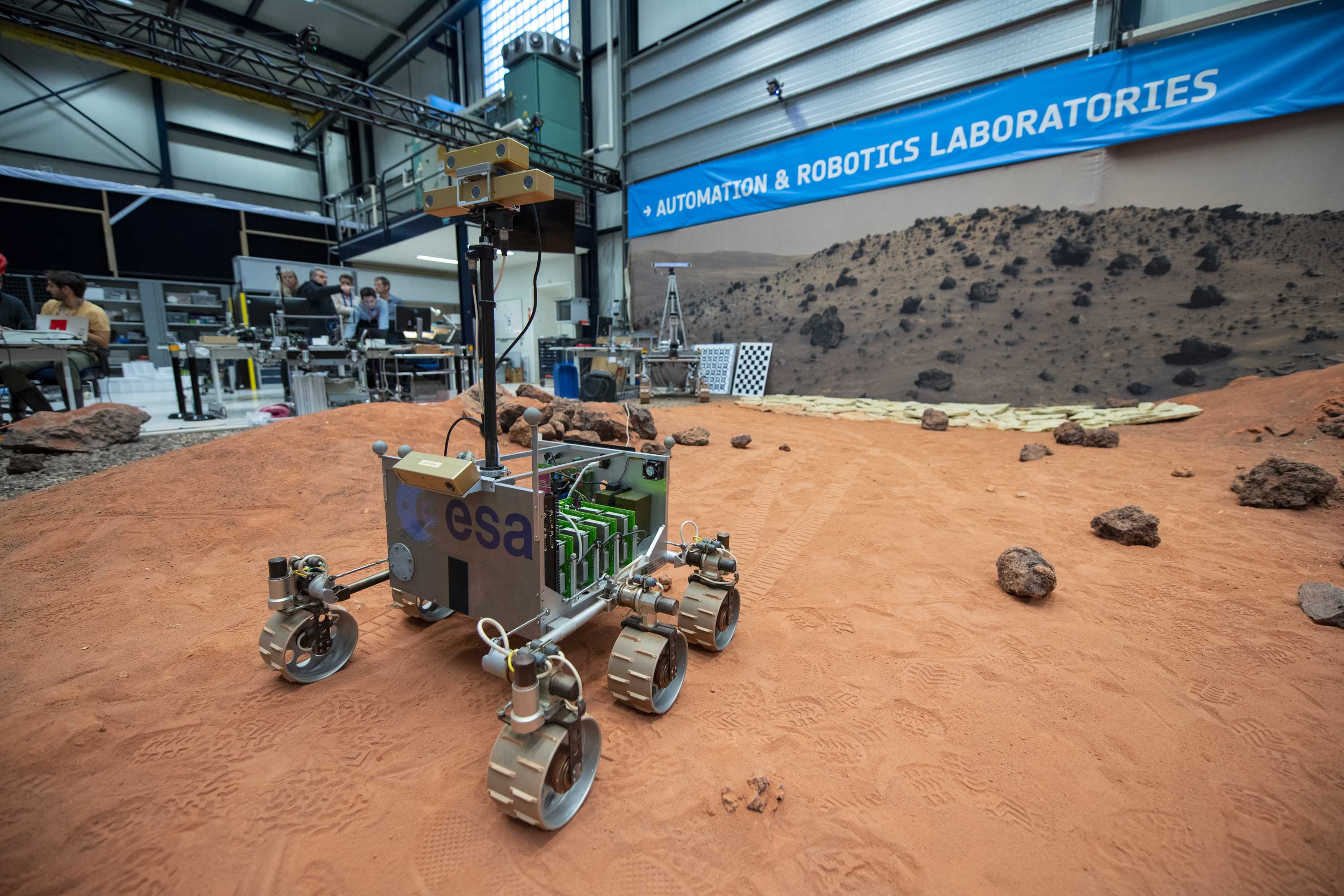
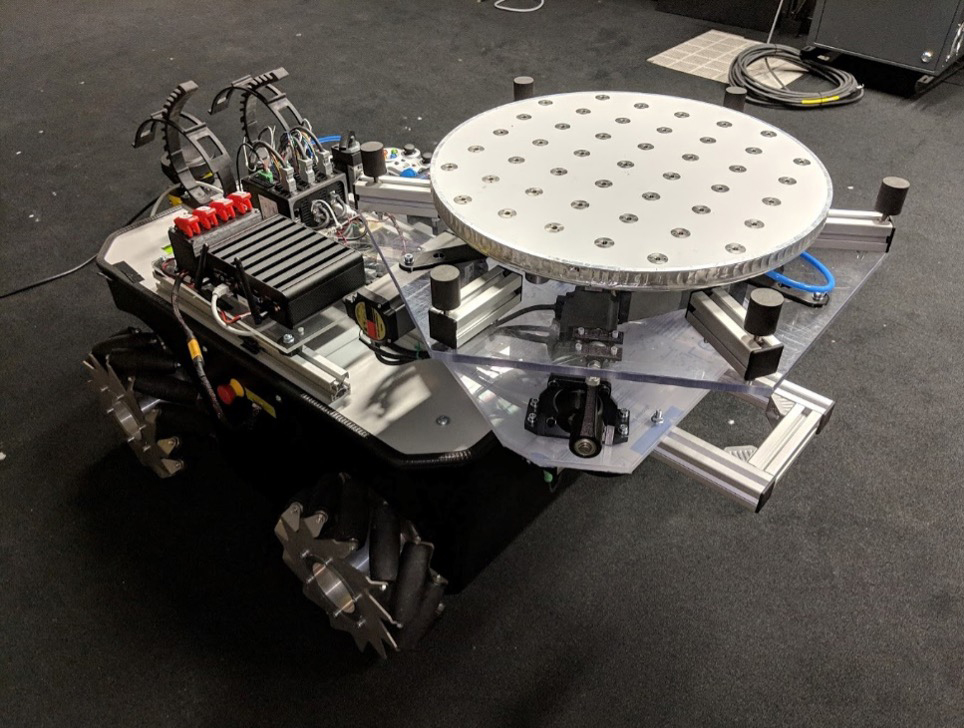
Planetary Robotics Lab
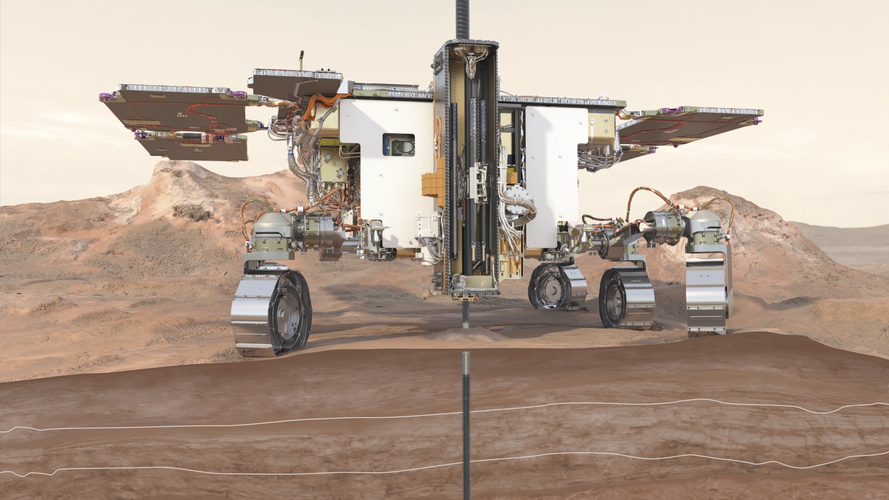
ESA's Planetary Robotics Laboratory is an engineering research laboratory that specialises in the challenges that robotic probes face in the exploration of the surface of Moon and Mars.
The Mars-analogue yard is a 9 m by 9 m ‘sandbox’ terrain filled with different sizes of sand, gravel and rock. Here, small to mid-size rovers can be tested to demonstrate locomotion and navigation capabilities on a planetary surface.
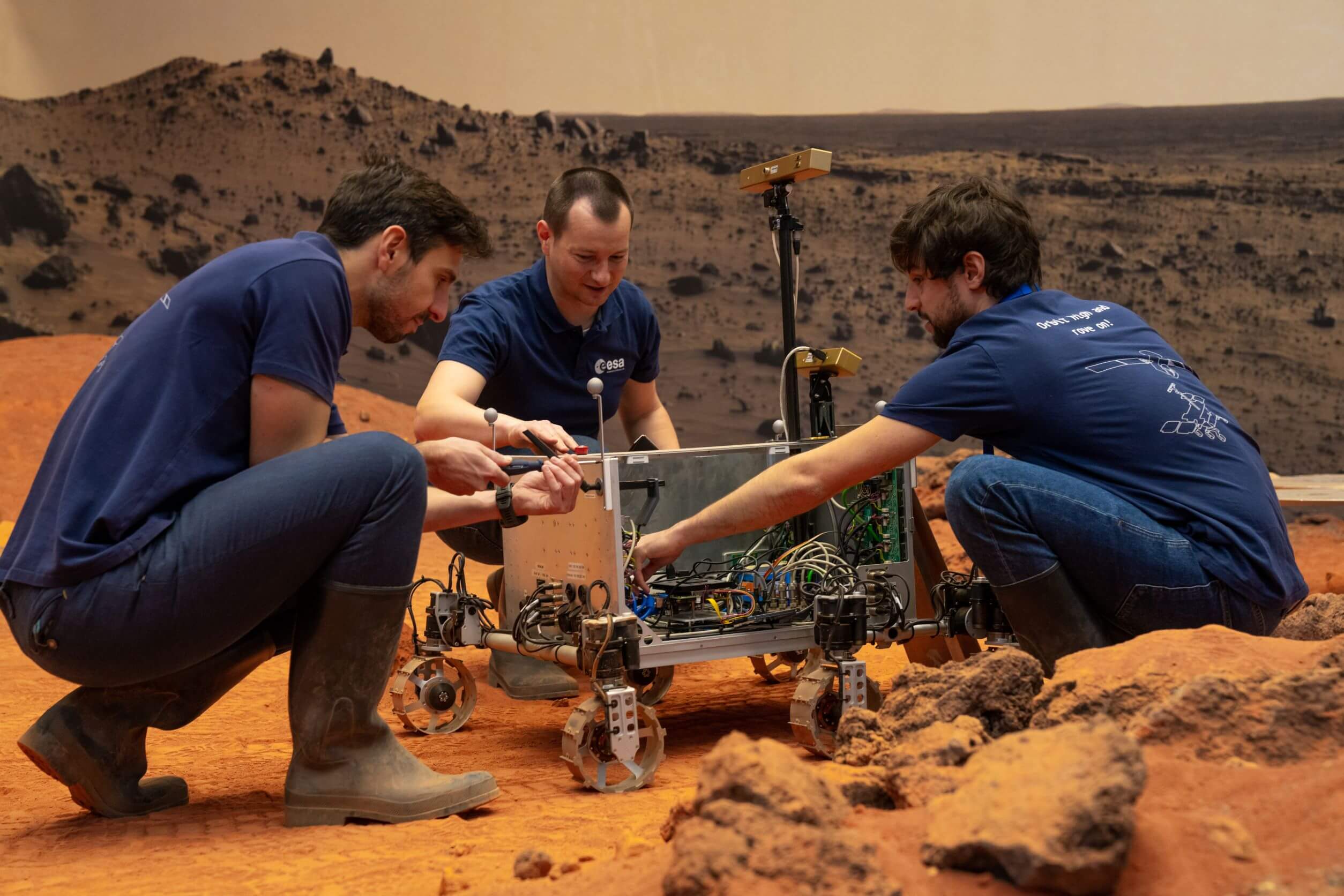
The lab developed and maintains multiple rover testbeds to investigate rover locomotion, perception and autonomy, together with operational aspects. Additionally, the lab features an industrial robotic arm with six degrees of freedom and a payload capacity of 130 kg as well as state-of-the-art measurement equipment for motion capture and 3D scanning.
SERVICES
Testing
- Performance evaluation
- Test beds development
- Characterisation
- Navigation/Localisation
- Human in the loop
- Contact Dynamics
Measurements
- Prototyping
- Motion capture, Robot Calibration
Simulation
- Modelling
- Virtual Simulation
Analysis
- Terramechanics analysis
- Surface Mission Analyses
- Human-Roboty interaction/Huma factors
- RVD Operation Analysis
Technical Assessment
- Consultancy
- Training
Simplified Access to Labs
- Large/Fast/Small Planetary Rovers, Motion Capture System
- Motion Capture System
- Full Suite for Field Testing (Including Transportation Vans, Generators, Control Computers, Differential GPS, Laser 3D Scanner, Map-Acquisition Drones)
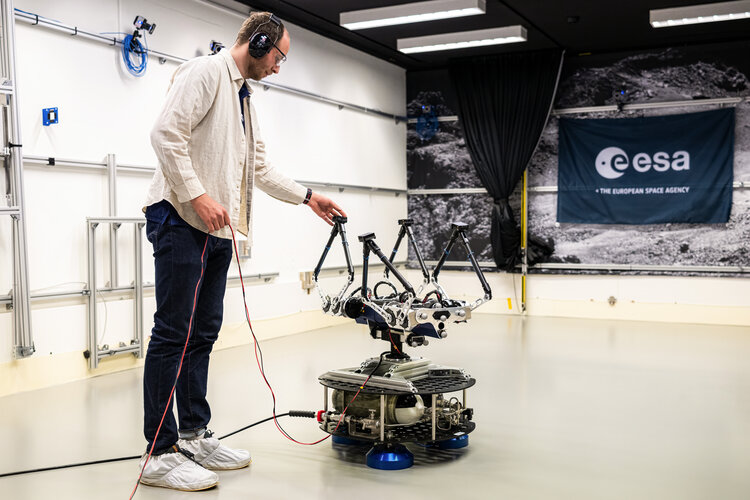
Human Robotics Interaction Lab
This laboratory is developing robotic technologies for advanced human-machine interaction. The focus is on real-time teleoperation of complex robotic systems and force feedback controls. The activities in the lab are creating and maintaining an industrial technology base for conducting space-based operations where robotic elements are remotely operated.
The laboratory regularly works with external partners and is experience in payload development for the ISS and conducting affiliated on-board experiments and operations . Its team is equipped for the rapid development of hardware and software systems, responding on a rapid turnaround basis to customer needs including the design and supply of specialised items to industry for specific projects or in the field testing, including spaceflight. Collaboration with non-space partners is also feasible, such as the offshore or nuclear industries.
The Lab possesses ISO 9001 certification for research and development, As so much of the Lab’s specialised equipment is at the forefront of technology, it has been designed, and often created, in house.
The ESA HRI laboratory has spaceflight proven competence in telerobotics, particularly with the use of haptic feedback and a history of research and development in robot exoskeletons for space use.
WE CAN HELP YOU GET THE BEST OUT OF OUR LABORATORIES
FOR FURTHER INFORMATION REGARDING THE ACCESS TO THE LABORATORY
Contact us via Email