Harmonisation
Technology Harmonisation provides all European actors with the framework and the key instruments needed to coordinate space technology at the European level.
This is achieved by identifying the needs and existing capabilities within Europe – as documented in Technology Harmonisation Dossiers – and by agreeing on ‘European Space Technology Roadmaps’, through a process of concertation, coordination and agreement between all participants. These joint Roadmaps aim at optimising public funding and guiding developments to ensure the right technology is at the right level of maturity at the right time.
The process has been developed to achieve better-coordinated research and development activities among actors in the European space sector, establishing a strong technology base as a means of underpinning the worldwide competitiveness of European industry and ensuring the success of future space missions.
Through nearly two decades of operation, and several major reviews that recommended its strengthening, Technology Harmonisation is now an established and well-proven European process. It involves over 1,000 European stakeholders, including ESA, national agencies and organisations, the European Commission, the European Defence Agency, and Space Entities (industry, R&D organisations, academia and associations).
In the scope of Harmonisation, space technologies are currently grouped into 48 topics, covering a wide range of subjects, from electric propulsion and de-orbiting technologies to optical communications and microelectronics. Topics are continuously evolving to recognise the dynamic nature of the space sector and emerging technology trends.
MAIN OBJECTIVES
"Fill strategic gaps" and "Minimise unnecessary duplications"
Consolidate European Strategic Capabilities
Achieve a Coordinated and Committed European Space technology Policy and Planning
Contribute to continuity and coherence between technology and industrial Policies
ESA TECHNOLOGY HARMONISATION ADVISORY GROUP - THAG

THAG is an ESA delegate body, established in 2006 to advise the ESA Industrial Policy Committee (IPC) on Technology Harmonisation matters, including:
- Technology harmonisation work plans
- Mapping of European capabilities with respect to the needs of the institutional and commercial markets
- Implementation within ESA programmes of agreed roadmaps and conclusions, and identification of national-and European-level funding
- Harmonisation measures to be applied in institutional programmes and by industry
HOW IT WORKS
ESA's Technology Coordination and Planning Office, supervises and coordinates all phases of the Harmonisation process to ensure European space technologies are aligned and strategically developed. Here's how the process works:
- Annual Topics: each year, up to 10 topics are selected for the Harmonisation. These topics are selected based on the last year of revisit, strategic needs and stakeholder input. They are reviewed and updated approximately every 4-5 years.
- Preparation of Dossier: ESA technical experts prepare Technology Harmonisation Dossiers (THDs) for each topic. These documents include strategic objectives, current capabilities and gaps, as well as future technology needs. They are shared with stakeholders via the Harmonisation Document Management System (HDMS)
- Internal coordination: ESA ensures alignement across technical, strategic and programmatic areas. This guarantees that roadmaps are consistent with ESA's long-term plans and mission requirements.
- External Coordination: the European and Canadian space community participates through open consultation rounds, held two times per year allowing stakeholders to review and comment on draft technology harmonisation dossiers including strategic roadmaps.
This process ensures coherence in technology development across Europe, efficient use of resources by avoiding duplication, timely availability of technologies for future missions.
How to participate
The European Space Technology Harmonisation is a voluntary process, based on transparency and exchange of information. Continuous support from all participants is crucial to the success of this European initiative.
European and Canadian Space Entities are invited to join Harmonisation including:
- Industry
- R&D Organisations and Academia
- Associations
Whether actively participating or not, the results are available to all stakeholders.
Space Entities may submit their inputs on the different technologies addressed during the consultation rounds through one of the channel listed below.
DIRECT PARTICIPATION
on ESA STAR Update your:
- Technology profile
- Entity capability responsible
You will be invited to participate to the consultation and harmonisation meeting when the topic corresponds to your entity capability areas of expertise
PARTICIPATION THROUGH THE NATIONAL DELEGATE
REMAIN IN CONTACT WITH YOUR NATIONAL DELEGATE
The THAG Delegate may recommend how to proceed further.
If you need the contact details of your THAG Delegate, please contact us

Access to Harmonisation Documentation
As a European or Canadian entity, you can request access to the harmonisation database on the Eclipse Polaris platform.
Harmonisation Process phases
Ongoing Harmonisation Cycles - topics and key dates
2026 Topics
Cycle 1 - Consultation Phase
Cycle 2
Actuators Building Blocks for Mechanisms
Ground Station Technology
Pyrotechnic Devices (within release mechanisms)
On-Board Computers, Data Handling Systems and Microelectronics
Printed Circuit Boards and Electronic Assembly Technologies
Avionics Embedded Systems
Additive Manufacturing
On-Board Software
Micro and Nano Technologies – MEMS Pressure Sensors, MOEMS and RF-MEMS
Radiation Environment and Effects
2026 Dates
Cycle 1
Cycle 2
Dec 2025
Feb 2026
Space Entities Consultation Start
17-19 Feb 2026
19-21 May 2026
Harmonisation Meeting
Jul 2026
Dec 2026
Dossiers Publication
2025 TOPICS
Cycle 1 - Published
Cycle 2 - Published
On-Board Radio Navigation Receivers
Power Management and Distribution
Critical Active RF Technologies
Power RF Measurements and Modelling
Enabling Artificial Intelligence for Space System Applications
Solar Array Drive Mechanisms
TT&C Transponders and Payload Data Transmitters
Solar Generators and Solar Cells
Functional Verification and Mission Operaions Systems
Harmonisation topics
Reflector Antennas
Last harmonised in 2023.
Reflector antennas are by far the most used type of antennas for space and often remain the best solution for applications with a single high gain beam or with multiple beams over a narrow field of view. Reflector antennas provide gain from a simple reflecting surface and can operate at multiple frequencies with single or multiple beams and they can also be shaped to provide one or more contoured beams.
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier (THD) and Roadmap can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.

Solar Array Drive Mechanisms
Currently in Harmonisation. Publication expected in Q4 2025.
Technologies included in this topic are those listed below.
- Motor: driving line or rotary actuator
- Stepper motors and brushless DC motors (see Actuator Building Blocks for Mechanisms)
- Bearings
- Lubrication
- Electrical transfer unit
- Flex harness, twist capsule, cable wrap technologies (limited rotation angle range)
- Slip ring technologies (not limited rotation angle range)
- Cylindrical or pancake/disk geometry for the slip rings
- Single-wire, braided-wire, flexible blades carrying contact blocks as brush geometries (integral electrical interfaces or “flying lead” for customer interfacing)
- V-grooved or flat tracks
- Brush-track material pairs
- Roll rings
- Contactless power and data transfer units
- Angular position and reference sensors (see the Harmonisation topic “Actuator Building Blocks for Mechanisms”)
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier (THD) and Roadmap can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.

Solar Generators and Solar Cells
Currently in Harmonisation. Publication expected in Q4 2025.
This topic covers the solar generator subsystem, which can be split into 4 design categories and an environmental testing category.
- Solar cells (with and without integral protection diode).
- Solar cell assemblies: solar cells with interconnectors and cover-glass, and discrete solar cell protection diode (when cell integrated diodes are not the preferred choice).
- Photovoltaic assembly: including mainly solar cell string, diodes, resistors, thermistors, harness, connectors and optical surface reflectors representing the integrated electrical part of the solar generator.
- Solar array assembly, enveloping the photovoltaic assembly, structural and mechanical parts of the generator.
- Environmental interaction of the solar generator with other subsystems, such as effects from radiation, atomic oxygen, thruster plume (chemical and electrical) and electrostatic discharge.Most artificial satellites, with a few exceptions, rely on the power generated by photovoltaic solar generators. This topic covers the solar generator subsystem, which can be split into 4 design categories and an environmental testing category.
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier (THD) and Roadmap can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.

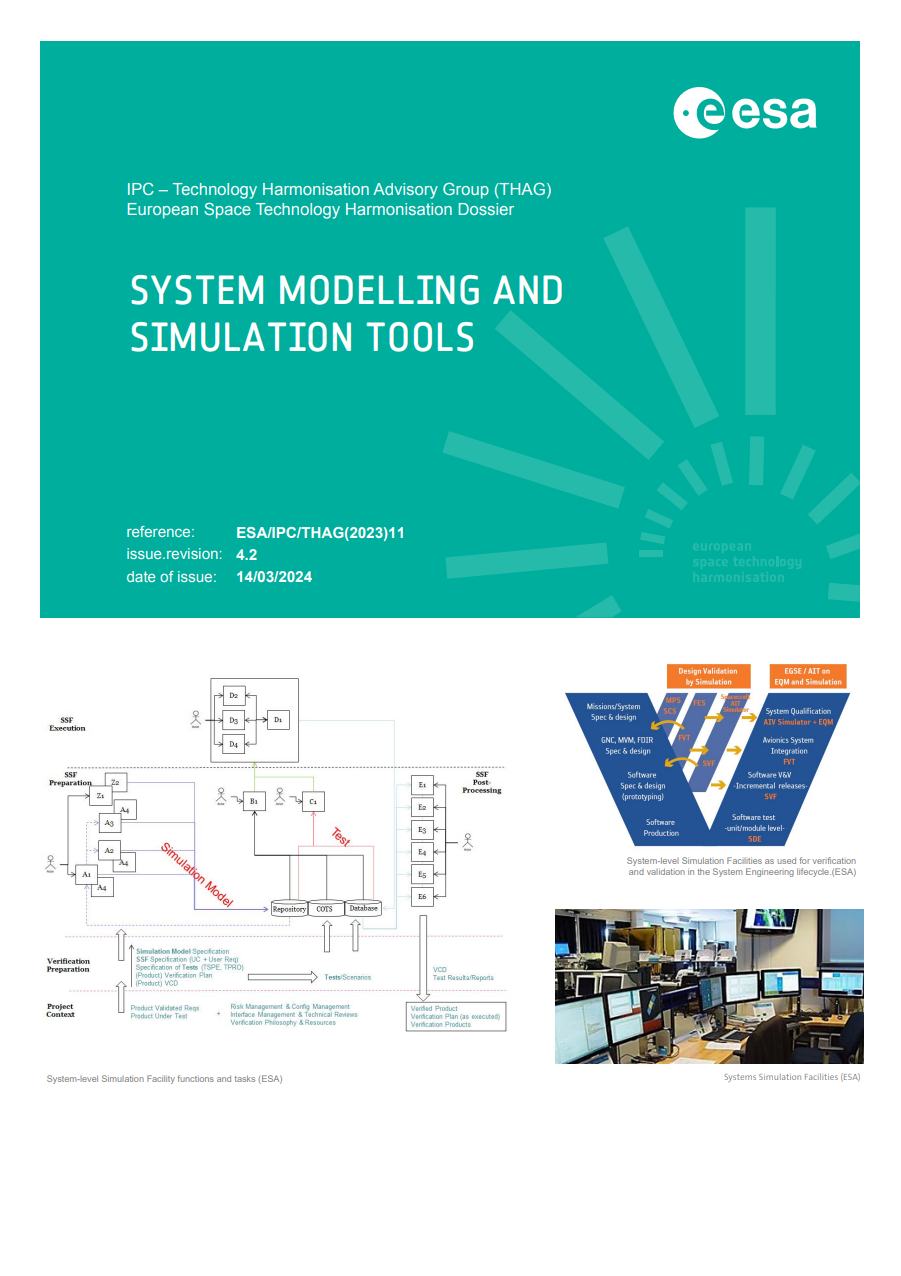
System Modelling & Simulation Tools
Last Harmonised in 2023.
This topic is considered a subset of the System Design and Verification domain, which includes technology, methods, and tools to support the System Engineering processes (specification, design, and verification) of space systems during the complete lifecycle of space missions (phases 0 to F). In particular it covers the items below.
- Space system lifecycle and system-level simulation facilities
- System concept simulator
- Mission performance simulator
- Functional engineering simulator
- Software validation facility
- Functional verification bench
- Assembly, integration and verification simulator
- Ground system test simulator
- Training, operations and maintenance simulator (TOMS).
- Digital twin spacecraft
- System-level modelling and simulation tasks
- Modelling phase (A)
- Software development phase
- Configuration setup phase (B)
- Configuration package setup phase (C)
- Simulation execution phase (D)
- Data processing and archiving phase (E)
- Database and repository function
Virtual system model, reference architecture and standards
- Simulation models and modelling methods: e.g. system dynamics, non-casual, discrete event, agent based, finite state machine, fact based/objects role modelling)
- Tooling
- Virtual reality, augmented reality, and extended reality technologies
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier (THD) and Roadmap can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.
Technologies for Hold Down, Release, Separation and Deployment Mechanisms
Last harmonised in 2021.
Most spacecraft have appendages (e.g. solar arrays, antenna reflectors, sensors, booms) that are stowed during launch and released once in orbit. To secure and enable these appendages, two types of mechanisms may be used: Hold-Down and Release Mechanism (HDRM) and the Deployment Mechanism (DM). This topic addresses building blocks of such mechanisms:
Hold Down and Release Mechanisms:
- Clamp bands and dispensers
- Non-explosive release actuators
- Magnetic clamp
- Pin puller / pusher
- Shape Memory Alloy
- Fusible wire / split spool
- Thermal cutter
- Bi-metallic actuator
Deployment Mechanisms:
- Dampers (viscous, melting alloy, Eddy current, magneto-rheological fluid)
- Shape Memory Alloy
- Escapement mechanism speed regulator
- Tape spring
- Magnetic bearing
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier (THD) and Roadmap can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.

Technologies for Optical Passive Instruments – Stable and Lightweight Structures, and Mirrors
Last Harmonised in 2024.
Mirrors are a small subset of passive optical components, but essential for the success of many space missions. They are involved in every new design or development of space instrumentation. Highly stable and lightweight structures are complimentary to the production of optical and scientific instruments for space missions. Such structures are needed to provide stable support to the components an optical system (e.g. mirrors, lenses, filters, prisms), detector assemblies (e.g. focal plane arrays, photodetectors) and supporting hardware and structures (e.g. mounts, optical benches and telescope structures). This topic covers the areas listed below.
- Deployable mirrors
- Deformable mirrors
- New mirror materials (e.g. ceramics, carbon nanotubes)
- Mirror steering mechanisms
- Metrology and verification methods
- Improvements in ultra-low CTE materials for ultra stable structures (e.g. Zerodur, SiN)
- Improvements in the characterisation of currently qualified materials (e.g. CTE characterisation of structural and optical materials at cryogenic temperatures)
- New manufacturing technologies (e.g. additive manufacturing of ceramics, joining of dissimilar materials or metals with dissimilar CTE like friction welding of Ti and Al)
- Improvements in the characterisation of thermos-elastic stability of additively manufactured structures such as optical benches, and improvements to facilities for verification of stable structures at cryogenic temperatures
Note that from Harmonisation 2024 this topic will combine the two former topics Technologies for Optical Passive Instruments – Stable and Lightweight Structures, and Technologies for Optical Passive Instruments – Mirrors.
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier (THD) and Roadmap can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK.
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.

Technologies for Passive Millimetre and Submilimetre Wave Instruments
Last Harmonised in 2024.
This topic deals with technologies needed for constructing passive instruments operating in a wide frequency range, extending from millimetre waves (30 – 300 GHz) to sub-millimetre waves (300 – 3000 GHz). In particular it covers all building blocks and the corresponding infrastructure needed to design, manufacture, test, evaluate and space qualify submillimetre wave instruments.
- Antenna reflector and reflector technology
- Antenna, receiver and subsystem measurements
- Mechanisms
- Relay optics, frequency selective structures, calibration loads and feeds
- Receivers, including mixers, LO and amplifiers
- Semiconductor devices and device technologies
- Spectrometers
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier (THD) and Roadmap can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.

TT&C Transponders and Payload Data Transmitters
Currently in Harmonisation. Publication expected in Q3 2025. Last Harmonised in 2020.
This topic covers the areas listed below.
- TT&C transponders for Near-Earth (NE) applications operating in S- (2 GHz) or X- (8 GHz) bands and using either standard phase modulation or spread spectrum technology. NE missions requiring higher data rates are increasingly using K-band (26 GHz) frequency band.
- TT&C transmitters, receivers and beacons (with in-orbit frequency selection) for telecommunication satellites
- Operating in C-, Ku- or Ka-band (in Earth Orbit GSO / NGSO), and Payload Control and Configuration transceivers. This covers both conventional (Frequency Modulation / Phase Modulation) and spread-spectrum approaches.
- Operating in X-, Ka- and EHF- (military) bands, using spread spectrum technology.
- TT&C transponders for Deep Space (DS) missions operating in the X- (8 GHz) and Ka- (32 GHz) bands.
- TT&C transponders for CubeSats and nanosats using S-, X- and K-band, and, more recently, lower bands like VHF (between 30MHz to 300MHz) and UHF (between 300MHz and 3GHz).
- Payload Data Transmitters dedicated to the transmission of science payload data.
- Other related areas
- Space-to-Space, Intersatellite or proximity TT&C links: Proximity transceivers (lander and orbiter) in S- and K- Bands in (cis)Lunar orbit and in UHF in DS planetary scenarios, Intersatellite link transceivers in S-Band, K- (NE) or Ka- Bands (DS)
- Launcher telemetry system
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier and Roadmap can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.
The European Space Technology Master Plan

The European Space Technology Master Plan (ESTMP) 2025 provides a comprehensive overview of Europe’s strategic approach to space technology development. Published for the ESA Ministerial Council 2025, this edition CM25 marks both the 50th anniversary of ESA and 25 years of the European Space Technology Harmonisation process.
The CM25 ESTMP Edition gives an overview on:
- Space Technology R&D budgets in Europe in 2024
- The structure and objectives of the new Harmonisation process, involving ESA, national agencies, industry, academia, and associations
- ESA Technology Programme landscape
- The drive for European non-dependence in critical technologies
- ESA Council at Ministerial level – CM25: ESA’s long-term strategy and vision for 2040, outlining goals for innovation, sustainability, and competitiveness
The ESTMP serves as a reference for stakeholders across Europe, supporting informed decision-making and fostering collaboration to ensure Europe remains at the forefront of space technology.
To access to the publication please contact us by email at estmp@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.




