Harmonisation
Technology Harmonisation provides all European actors with the framework and the key instruments needed to coordinate space technology at the European level.
This is achieved by identifying the needs and existing capabilities within Europe – as documented in Technology Harmonisation Dossiers – and by agreeing on ‘European Space Technology Roadmaps’, through a process of concertation, coordination and agreement between all participants. These joint Roadmaps aim at optimising public funding and guiding developments to ensure the right technology is at the right level of maturity at the right time.
The process has been developed to achieve better-coordinated research and development activities among actors in the European space sector, establishing a strong technology base as a means of underpinning the worldwide competitiveness of European industry and ensuring the success of future space missions.
Through nearly two decades of operation, and several major reviews that recommended its strengthening, Technology Harmonisation is now an established and well-proven European process. It involves over 1,000 European stakeholders, including ESA, national agencies and organisations, the European Commission, the European Defence Agency, and Space Entities (industry, R&D organisations, academia and associations).
In the scope of Harmonisation, space technologies are currently grouped into 48 topics, covering a wide range of subjects, from electric propulsion and de-orbiting technologies to optical communications and microelectronics. Topics are continuously evolving to recognise the dynamic nature of the space sector and emerging technology trends.
MAIN OBJECTIVES
"Fill strategic gaps" and "Minimise unnecessary duplications"
Consolidate European Strategic Capabilities
Achieve a Coordinated and Committed European Space technology Policy and Planning
Contribute to continuity and coherence between technology and industrial Policies
ESA TECHNOLOGY HARMONISATION ADVISORY GROUP - THAG

THAG is an ESA delegate body, established in 2006 to advise the ESA Industrial Policy Committee (IPC) on Technology Harmonisation matters, including:
- Technology harmonisation work plans
- Mapping of European capabilities with respect to the needs of the institutional and commercial markets
- Implementation within ESA programmes of agreed roadmaps and conclusions, and identification of national-and European-level funding
- Harmonisation measures to be applied in institutional programmes and by industry
HOW IT WORKS
ESA's Technology Coordination and Planning Office, supervises and coordinates all phases of the Harmonisation process to ensure European space technologies are aligned and strategically developed. Here's how the process works:
- Annual Topics: each year, up to 10 topics are selected for the Harmonisation. These topics are selected based on the last year of revisit, strategic needs and stakeholder input. They are reviewed and updated approximately every 4-5 years.
- Preparation of Dossier: ESA technical experts prepare Technology Harmonisation Dossiers (THDs) for each topic. These documents include strategic objectives, current capabilities and gaps, as well as future technology needs. They are shared with stakeholders via the Harmonisation Document Management System (HDMS)
- Internal coordination: ESA ensures alignement across technical, strategic and programmatic areas. This guarantees that roadmaps are consistent with ESA's long-term plans and mission requirements.
- External Coordination: the European and Canadian space community participates through open consultation rounds, held two times per year allowing stakeholders to review and comment on draft technology harmonisation dossiers including strategic roadmaps.
This process ensures coherence in technology development across Europe, efficient use of resources by avoiding duplication, timely availability of technologies for future missions.
How to participate
The European Space Technology Harmonisation is a voluntary process, based on transparency and exchange of information. Continuous support from all participants is crucial to the success of this European initiative.
European and Canadian Space Entities are invited to join Harmonisation including:
- Industry
- R&D Organisations and Academia
- Associations
Whether actively participating or not, the results are available to all stakeholders.
Space Entities may submit their inputs on the different technologies addressed during the consultation rounds through one of the channel listed below.
DIRECT PARTICIPATION
on ESA STAR Update your:
- Technology profile
- Entity capability responsible
You will be invited to participate to the consultation and harmonisation meeting when the topic corresponds to your entity capability areas of expertise
PARTICIPATION THROUGH THE NATIONAL DELEGATE
REMAIN IN CONTACT WITH YOUR NATIONAL DELEGATE
The THAG Delegate may recommend how to proceed further.
If you need the contact details of your THAG Delegate, please contact us

Access to Harmonisation Documentation
As a European or Canadian entity, you can request access to the harmonisation database on the Eclipse Polaris platform.
Harmonisation Process phases
Ongoing Harmonisation Cycles - topics and key dates
2026 Topics
Cycle 1 - Consultation Phase
Cycle 2
Actuators Building Blocks for Mechanisms
Ground Station Technology
Pyrotechnic Devices (within release mechanisms)
On-Board Computers, Data Handling Systems and Microelectronics
Printed Circuit Boards and Electronic Assembly Technologies
Avionics Embedded Systems
Additive Manufacturing
On-Board Software
Micro and Nano Technologies – MEMS Pressure Sensors, MOEMS and RF-MEMS
Radiation Environment and Effects
2026 Dates
Cycle 1
Cycle 2
Dec 2025
Feb 2026
Space Entities Consultation Start
17-19 Feb 2026
19-21 May 2026
Harmonisation Meeting
Jul 2026
Dec 2026
Dossiers Publication
2025 TOPICS
Cycle 1 - Published
Cycle 2 - Published
On-Board Radio Navigation Receivers
Power Management and Distribution
Critical Active RF Technologies
Power RF Measurements and Modelling
Enabling Artificial Intelligence for Space System Applications
Solar Array Drive Mechanisms
TT&C Transponders and Payload Data Transmitters
Solar Generators and Solar Cells
Functional Verification and Mission Operaions Systems
Harmonisation topics
On-board Radio Navigation Receivers
Last Harmonised in 2025.
This topic addresses various types of On-Board Radio Navigation Receivers and their core technologies, including those listed below.
- High reliability GNSS space receivers for high-end and mid-range performance: platform receivers to determine absolute and/or relative PVT, including on-ground or on-board precise orbit determination (POD).
- High-End Receivers: typically multi frequency receivers with meter level navigation accuracy and sub-decimetre accuracy in case of on-board real-time POD.
- Mid-Range Receivers: typically single frequency receivers with tens of meter level navigation accuracy with standard point positioning, reaching sub-meter accuracy with advanced orbital filter.
- EO/Scientific GNSS space receivers, such as for reflectometry and radio occultation instruments.
- Low Cost GNSS space receivers based on COTS parts and with limited reliability and level of qualification status, including products for CubeSats.
- Supporting GNSS core technologies: Radio Frequency analogue components (including complex MIMIC), Base-Band processing, clock, GNSS antennas, and technologies for detecting and mitigating interference and spoofing.
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier (THD) and Roadmap can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.

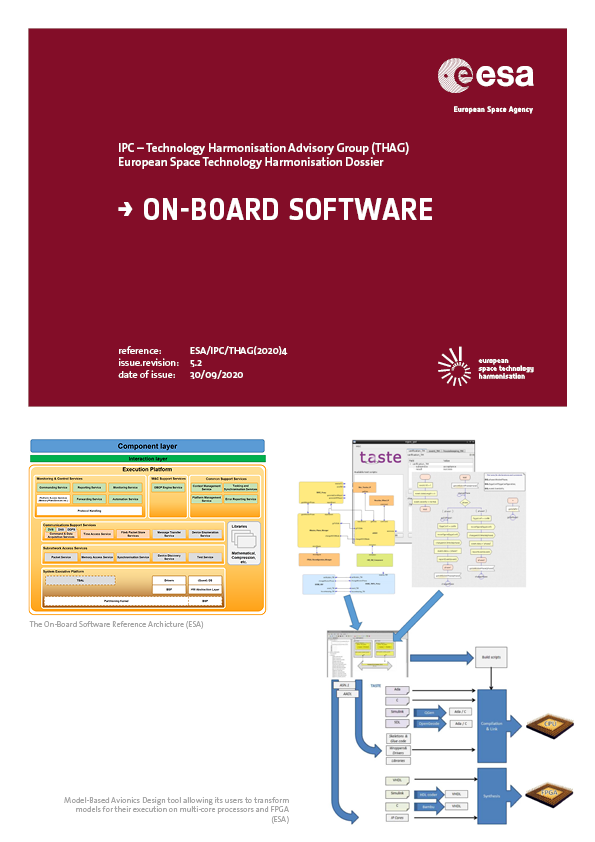
On-board Software
Last harmonised in 2020.
The space system on-board software consists of software (SW) applications embedded in space systems. It interfaces with the ground-based SW, which is developed to support daily operations after launch. The topic is organised around the domains listed below.
- Methods and tools for the SW development that are innovative in the commercial world and require analyses for the adoption in the space domain.
- New functions of the SW systems that are anticipated to be needed but that need pre-development or prototyping before actual space developments (autonomy, FDIR).
- Space Segment SW including:
- Methods and tools for On-Board SW engineering: all aspects of On-Board SW engineering, requirements, automation of the life cycle, testing, model based development, formal methods (programme verification, correctness proof of specific required properties, static schedulability analysis, etc). In particular, it includes SW simulators and emulators of on-board processors interfacing with System and SW engineering and respective tools.
- Innovative management processes: adaptive engineering, agile life cycle, new planning approaches, cost estimation methods, distributed development. Focus is on system aspects of SW, system SW co-engineering. Covers also SW-HW co-engineering.
- Architectures: Software architectures for space segment software, including TSP approach, communication protocols, Plug and Play technologies.
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier (THD) and Roadmap can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.
Optical Communications for Space
Last harmonised in 2022.
Optical communications use light to transmit data between two points. By replacing radio frequency signals with laser light as a means of carrying data, optical communication technologies offer great advantages for links between spacecraft or between spacecraft and the ground. This topic covers optical communication technologies where at least one of two partner terminals in a point-to-point communication link is embarked on a spacecraft.
- Space-borne terminals for inter-satellite links: LEO-LEO, MEO-HAPS, MEO-LEO, MEO-MEO, GEO-HAPS, GEO-LEO, GEO-GEO, Deep Space – Earth Orbit.
- Space-borne terminals for Space Direct-to-Earth (DTE) links: HAPS-DTE, LEO-DTE, MEO-DTE, GEO-DTE, Lunar-DTE, Deep Space – DTE.
- Ground-based terminals for Space Direct-to-Earth links: including steerable optical ground station feeder links to LEO/MEO, non-steerable optical ground station feeder links to GEO, quantum key distribution, and Moon-based optical ground station.
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier (THD) and Roadmap can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.

Optical Detectors
Last harmonised in 2022.
Detectors form the cornerstone of many space missions as they are used to sense radiation from infrared to X-rays and beyond, and often their performance is the limiting factor for instrumentation on board spacecraft. Within Harmonisation this topic focuses on optical detectors in the range from ultraviolet (UV) to visible and infrared (IR) wavelengths, with a main focus on the latter two.
- Silicon detectors operating in the waveband near UV to near IR (250-1000 nm):
- Charge-Coupled Devices (CCD)
- CMOS Image Sensors (CIS)
- UV to NIR photon-counting detector technologies: mainly Single-Photon Avalanche Diodes / Silicon Photomultiplier (SPAD/SiPM), Avalanche Photodiodes (APDs) and photocathode-based detectors.
- IR detectors operating in the spectral range from 1µm to ~20µm (and up to sub-mm in a few scientific applications): including MCTs, InGaAs, III-V compounds, Type-II super-lattice structures, uncooled thermal detectors, APDs and associated support electronic devices (ASICs).
This topic also looks into supply chain issues related to all applications.
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier (THD) and Roadmap can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.

Photonics
Last Harmonised in 2023.
Photonics is a term for a very broad field which involves the generation, manipulation and detection of light. This topic covers aspects of waveguided optics, in particular fibre optics and integrated optics for space application.
- Components: lasers for digital and analogue transmission, frequency combs, modulators, photodiodes for digital and analogue communications, opto-couplers, passives (single and multi-mode optical fibres, fibre optic couplers/splitters, multi/demultiplexers, isolators, connectors).
- Sub-systems: modulators, e.g. optical amplifiers.
- End-to-end links: digital and analogue
- Equipment: e.g. Frequency Generator Unit, frequency converter, router, RF filter, beam forming network, optical wireless, fibre sensing (fibre optic gyroscopes, thermal monitoring…), opto-pyrotechnics, micro-photonics, packaging
Note that hybrid devices and equipment used in LIDARs, laser communication terminals, Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) and optical clocks are covered in other Harmonisation topics. See in particular Optical Communications for Space, and Frequency and Time Generation and Distribution.
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier (THD) and Roadmap can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.
Power Management and Distribution
Currently in Harmonisation. Publication expected in Q4 2025.
Power management and distribution are crucial functions in satellite systems, as they ensure that all subsystems operate reliably. The power management system regulates the power supply, stores excess energy, and distributes it to the various subsystems as required. The distribution system provides the power to each subsystem while ensuring that the overall power usage remains within the limits of the satellite's power budget. The areas covered by this topic are listed below.
- Power subsystems architecture: including power subsystem topologies, sizing, modelling and simulation tools and techniques.
- Power electronics or power conditioning and distribution: including regulation, control and distribution within the spacecraft power subsystem (management of solar array power and battery storage including protection and distribution to the loads), and within any electrical equipment (power converters, distribution, protections).
- Basic materials and processes: including hardware and component technologies used in power conditioning and distribution and analogue domains.
- High voltage power management (>200V) and high voltage and high temperature potting materials for applications like power supplies for Travelling Wave Tubes, Electrical Propulsion electronics.
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier (THD) and Roadmap can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.

Power RF Measurement and Modelling
Currently in Harmonisation. Publication expected in Q4 2025.
This topic covers the main destructive phenomena related to spacecraft RF power, and the technologies available to prevent them or reduce the associated risks.
- Multipactor
- Corona or gas discharge
- Passive intermodulation interference between high-power transmission and low-power receiving antennae
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier and Roadmap (THD) can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.

Printed Circuit Boards and Electronic Assembly Technologies
Last harmonised in 2022.
Printed Circuit Boards and Electronic Assembly Technologies provide the interconnection and packaging technologies for EEE components to operate reliably and in unison within the electronic system. System level packaging by assembly of EEE parts on PCBs constitute the nerves and the veins of the electronic system, interconnecting its brains and senses by distributing power and signal. In addition, system packaging provides the backbone and armour, as the sensitive EEE parts need protection from the harsh environmental conditions of the soldering processes, ground-based testing, launch and prolonged operation in the application environment. The technology domain is strongly driven by reliability, miniaturisation, signal speeds, power integrity, thermal management, environmental legislation and commercial market trends. This Harmonisation topic covers printed circuit board materials, electronic assembly technologies and verification processes of the assemblies as well as harness manufacturing processes.
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier (THD) and Roadmap can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.
Pyrotechnic Devices
Last harmonised in 2020.
Pyrotechnic devices, in the context of release mechanisms, refer to the category of devices that utilise the energy released from a controlled explosion to perform useful work. Pyrotechnic devices are used in many crucial single-use operations in a space mission. This topic includes areas listed below.
- Cords
- Cutters
- Separator nuts
- Detonating transfer lines
- Detonators (including opto-pyro detonators)
- Pyrovalves
- Shock generators
- Microperforators
- Thruster igniters
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier (THD) and Roadmap can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.

Radiation Environment and Effects
Last harmonised in 2021.
Radiation effects on spacecraft are an increasing problem, due to the increasing complexity of spacecraft platforms and payloads as well as the changing nature of missions (longer traverse time in radiation belts, more hazardous locations). Here radiation refers to particle radiation (highly energetic plasma) with a nominal energy range from 30 keV to >10 MeV (electrons) and 0.1 MeV/nucleon to > 1 GeV/nucleon (protons and heavier ions). This topic covers radiation:
- environment measurement techniques,
- environment modelling,
- effects analysis tools,
- hardening and radiation effects mitigation,
- effect mechanisms,
- effects testing methods,
- facilities,
- hardness assurance.
The Technology Harmonisation Dossier (THD) and Roadmap can be accessed via our Harmonisation Document Management System under the following links: THD LINK / Roadmap LINK
If you do not have an account yet, you may request one by sending an email to harmo@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.

The European Space Technology Master Plan

The European Space Technology Master Plan (ESTMP) 2025 provides a comprehensive overview of Europe’s strategic approach to space technology development. Published for the ESA Ministerial Council 2025, this edition CM25 marks both the 50th anniversary of ESA and 25 years of the European Space Technology Harmonisation process.
The CM25 ESTMP Edition gives an overview on:
- Space Technology R&D budgets in Europe in 2024
- The structure and objectives of the new Harmonisation process, involving ESA, national agencies, industry, academia, and associations
- ESA Technology Programme landscape
- The drive for European non-dependence in critical technologies
- ESA Council at Ministerial level – CM25: ESA’s long-term strategy and vision for 2040, outlining goals for innovation, sustainability, and competitiveness
The ESTMP serves as a reference for stakeholders across Europe, supporting informed decision-making and fostering collaboration to ensure Europe remains at the forefront of space technology.
To access to the publication please contact us by email at estmp@esa.int from a corporate email address providing business affiliation and position in the company.




